| opt_table_font {gt} | R Documentation |
Options to define font choices for the entire table
Description
opt_table_font() makes it possible to define fonts used for an entire
gt table. Any font names supplied in font will (by default, with
add = TRUE) be placed before the names present in the existing font stack
(i.e., they will take precedence). You can choose to base the font stack on
those provided by system_fonts() by providing a valid keyword for a themed
set and optionally prepending font values to that.
Take note that you could still have entirely different fonts in specific
locations of the table. For that you would need to use tab_style() or
tab_style_body() in conjunction with cell_text().
Usage
opt_table_font(
data,
font = NULL,
stack = NULL,
weight = NULL,
style = NULL,
add = TRUE
)
Arguments
data |
The gt table data object
This is the gt table object that is commonly created through use of the
|
font |
Default table fonts
One or more font names available as system or web fonts. These can be
combined with a |
stack |
Name of font stack
A name that is representative of a font stack (obtained via internally via
the |
weight |
Text weight
Option to set the weight of the font. Can be a text-based keyword such as
|
style |
Text style
An option to modify the text style. Can be one of either |
add |
Add to existing fonts
Should fonts be added to the beginning of any already-defined fonts for the
table? By default, this is |
Value
An object of class gt_tbl.
Possibilities for the font argument
We have the option to supply one or more font names for the font argument.
They can be enclosed in c() or a list(). You can generate this list or
vector with a combination of font names, and you can freely use
google_font(), default_fonts(), and system_fonts() to help compose
your font family.
Possibilities for the stack argument
There are several themed font stacks available via the system_fonts()
helper function. That function can be used to generate all or a segment of a
vector supplied to the font argument. However, using the stack argument
with one of the 15 keywords for the font stacks available in
system_fonts(), we could be sure that the typeface class will work across
multiple computer systems. Any of the following keywords can be used:
-
"system-ui" -
"transitional" -
"old-style" -
"humanist" -
"geometric-humanist" -
"classical-humanist" -
"neo-grotesque" -
"monospace-slab-serif" -
"monospace-code" -
"industrial" -
"rounded-sans" -
"slab-serif" -
"antique" -
"didone" -
"handwritten"
Examples
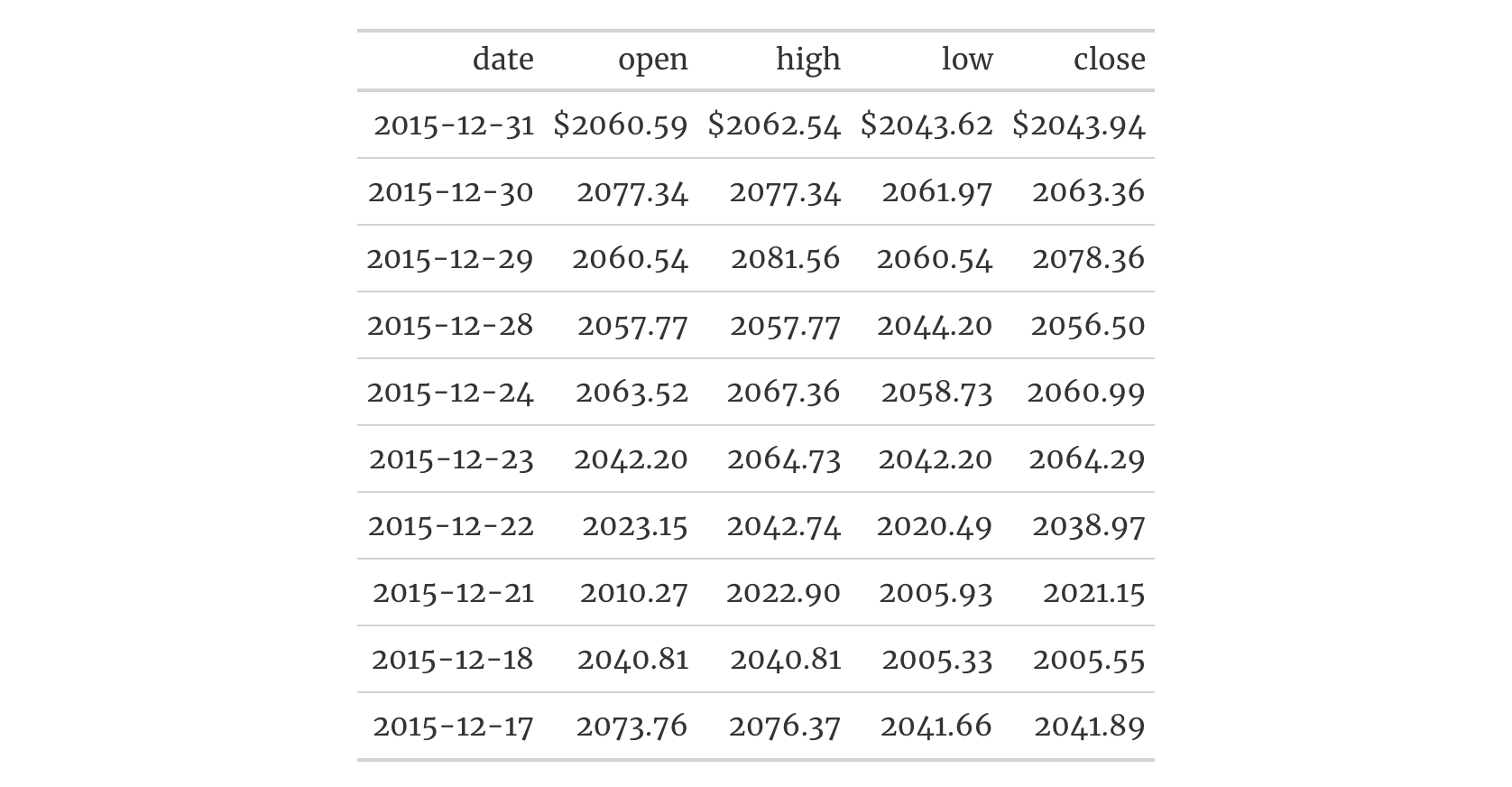
Use a subset of the sp500 dataset to create a small gt table. We'll
use fmt_currency() to display a dollar sign for the first row of monetary
values. Then, set a larger font size for the table and use the
"Merriweather" font (from Google Fonts, via google_font()) with two
system font fallbacks ("Cochin" and the generic "serif").
sp500 |>
dplyr::slice(1:10) |>
dplyr::select(-volume, -adj_close) |>
gt() |>
fmt_currency(
rows = 1,
use_seps = FALSE
) |>
opt_table_font(
font = list(
google_font(name = "Merriweather"),
"Cochin", "serif"
)
)
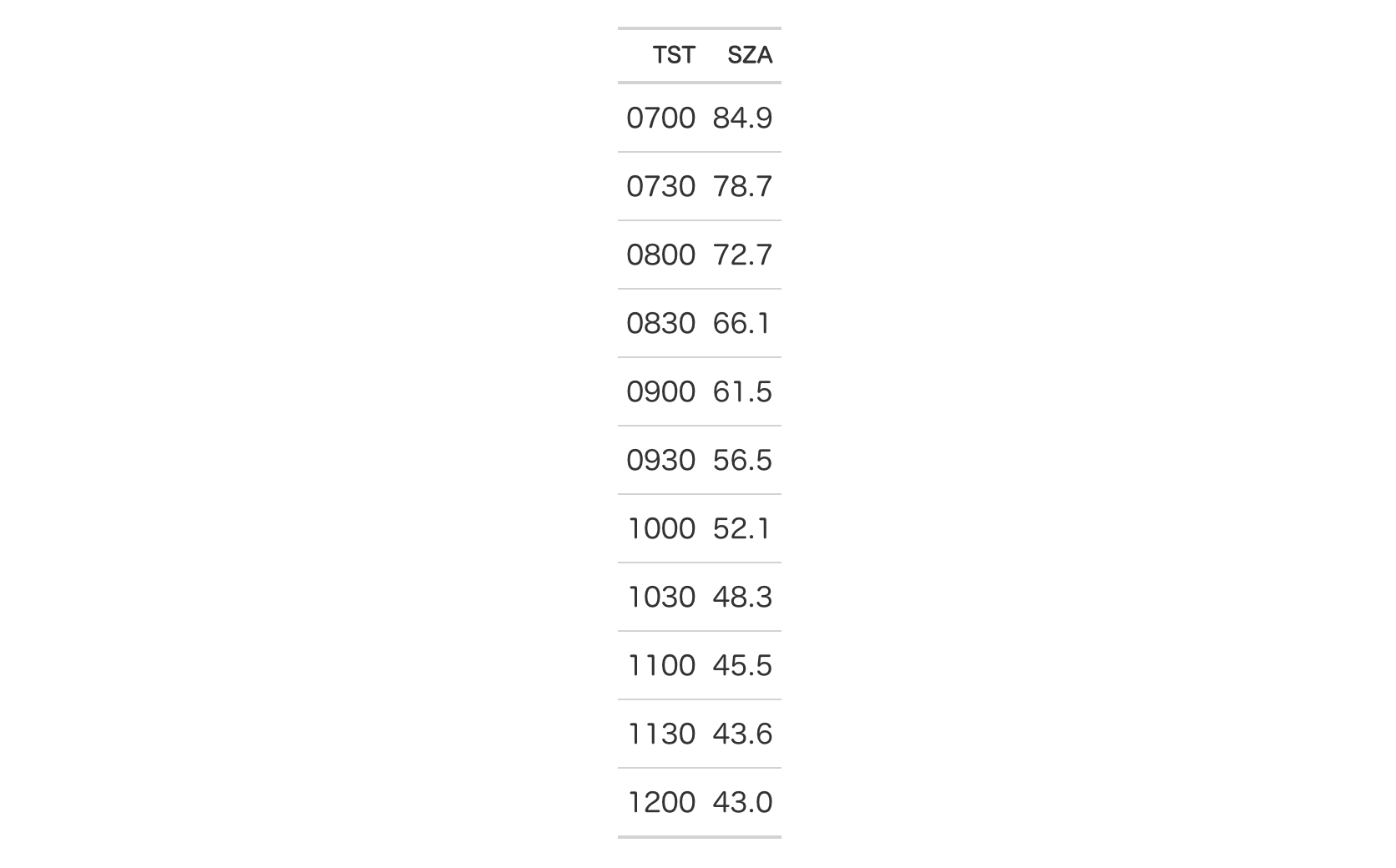
With the sza dataset we'll create a two-column, eleven-row table. Within
opt_table_font(), the stack argument will be supplied with the
"rounded-sans" font stack. This sets up a family of fonts with rounded,
curved letterforms that should be locally available in different computing
environments.
sza |>
dplyr::filter(
latitude == 20 &
month == "jan" &
!is.na(sza)
) |>
dplyr::select(-latitude, -month) |>
gt() |>
opt_table_font(stack = "rounded-sans") |>
opt_all_caps()
Function ID
10-12
Function Introduced
v0.2.2 (August 5, 2020)
See Also
Other table option functions:
opt_align_table_header(),
opt_all_caps(),
opt_css(),
opt_footnote_marks(),
opt_footnote_spec(),
opt_horizontal_padding(),
opt_interactive(),
opt_row_striping(),
opt_stylize(),
opt_table_lines(),
opt_table_outline(),
opt_vertical_padding()